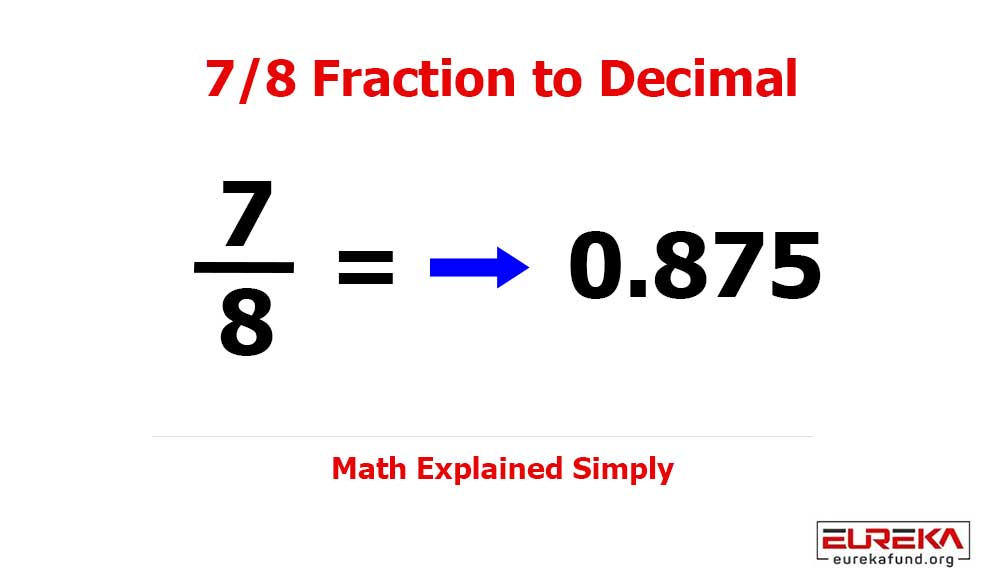
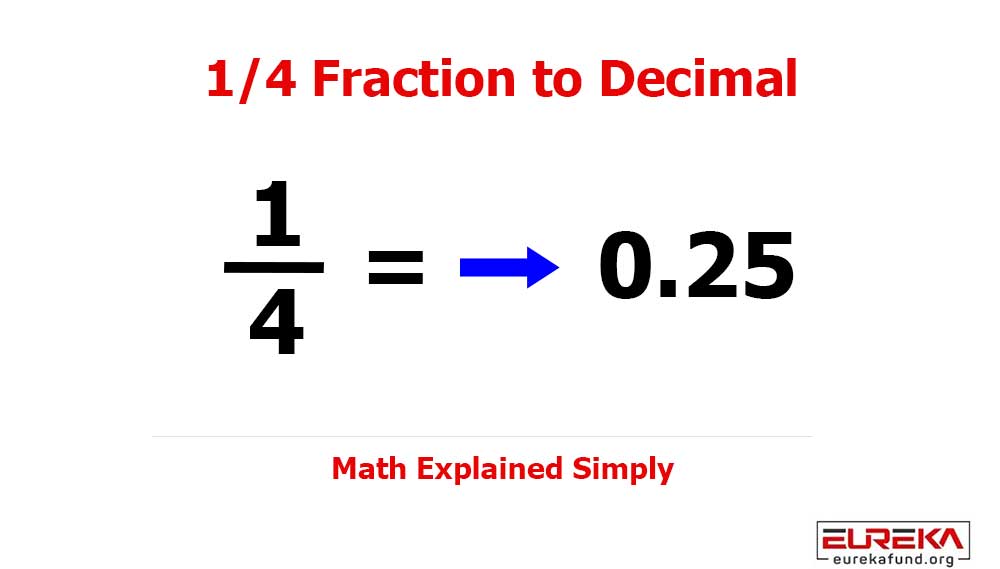
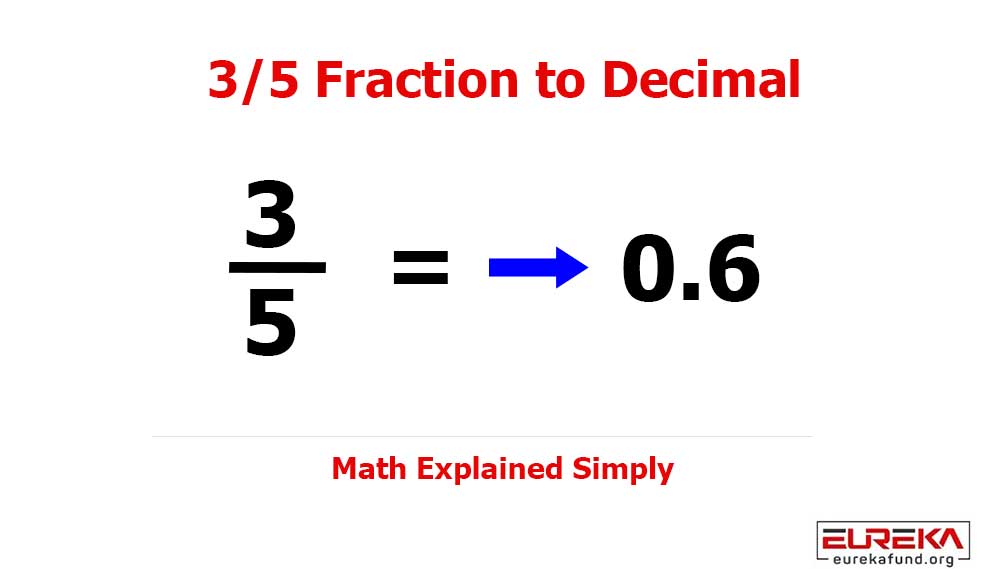
The last decade transformed the world at lightning speed — from smart cars to medical automation, from IoT platforms to AI-driven devices. In 2025, embedded software systems have shifted from being a competitive advantage to an absolute necessity for industries aiming to stay modern, efficient, and profitable.
Embedded software is the invisible engine running inside nearly every smart device today — from your car’s braking system to your smartwatch, ATM machines, medical ventilators, drones, and manufacturing robots. As industries push toward hyper-automation and IoT-driven infrastructure, embedded systems have become the foundation of digital transformation.
What Are Embedded Software Systems?
Embedded software refers to specialized programs engineered to run inside hardware devices—powered by microcontrollers, microprocessors, and chips. These systems are designed to deliver:
- Real-time decision making
- Precision control
- High-speed automation
- Low-power, optimized performance
- Seamless integration with sensors, cloud, and IoT platforms
In short: No modern device runs without embedded software.
Industries using embedded systems in 2025 include:
- Automotive & EVs
- Consumer electronics
- Industrial equipment & robotics
- Banking & ATMs
- Healthcare devices
- Smart home tech
- Telecom
- Aerospace
Why Embedded Software is Non-Negotiable in 2025
1. Critical for Automotive & Electric Vehicle (EV) Industry
The automotive industry is now fully dependent on embedded systems. Modern cars rely on micro-software for:
- Autonomous driving
- Parking sensors
- Cruise control
- Smart dashboards
- Battery management (for EVs)
- Brake & safety systems

EV manufacturers in 2025 hire embedded engineers as a core part of their product teams because embedded software directly influences:
- Customer safety
- Performance efficiency
- Energy savings
- User satisfaction
For EVs and smart vehicles — embedded software is the brain behind the machine.
2. Essential for Healthcare & Life-Saving Medical Devices
The pandemic accelerated demand for automated medical devices. Today, embedded systems power:
- Ventilators
- Infusion pumps
- ECG machines
- Ultrasound scanners
- Insulin pumps
- Diagnostic instruments
Healthcare requires real-time performance. Embedded systems provide:
- Precision
- Speed
- Low failure rate
- High reliability
This makes embedded solutions indispensable for life-saving operations.
3. Improved Real-Time Scheduling & Priority Processing
Embedded systems support real-time operating systems (RTOS) to manage time-critical operations. This allows businesses to:
- Prioritize tasks
- Reduce processing delays
- Improve system performance
- Support multitasking with accuracy
According to global research forecasts, the RTOS market is expected to grow sharply by 2027, driven by automation and rising IoT adoption.

Major Benefits of Embedded Software Solutions
Here’s why industries are rushing to embed software into their products:
High scalability
Easily expandable with new features, firmware updates, or hardware additions.
Ultra-fast performance
Designed for speed, reliability, and minimal latency.
Precision control
Ideal for mission-critical tasks—medical, automotive, and manufacturing.
Multi-tasking abilities
Handles simultaneous operations efficiently.
Lower power consumption
Optimized for long-term usage in portable and battery-powered devices.
Accurate, error-free output
Pre-programmed logic ensures consistent execution.
Enhanced innovation
Enables companies to launch cutting-edge smart devices.
Better customer experience
Embedded applications help track user data, improve personalization, and deliver smart alerts.
Dominance in IoT & smart device market
Embedded systems are the backbone of all IoT ecosystems.
Conclusion
Embedded software solutions are no longer optional—they are the foundation of modern digital products. From vehicles and healthcare machinery to banking systems and smart home devices, embedded technology enables innovation, precision, cost efficiency, and next-generation user experience.
If a business delays adopting embedded technologies, it risks falling behind competitors, losing customers, and missing future growth opportunities.