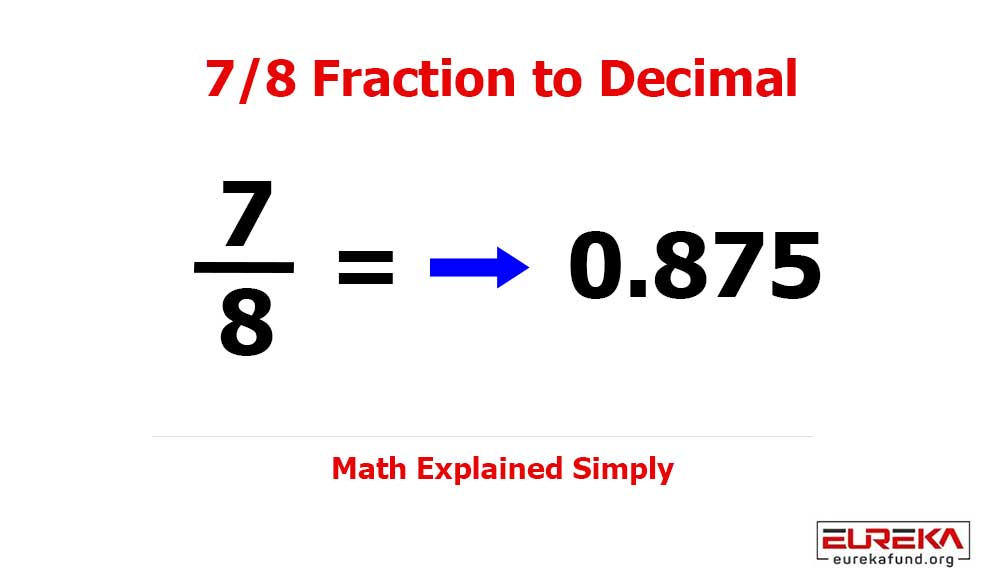
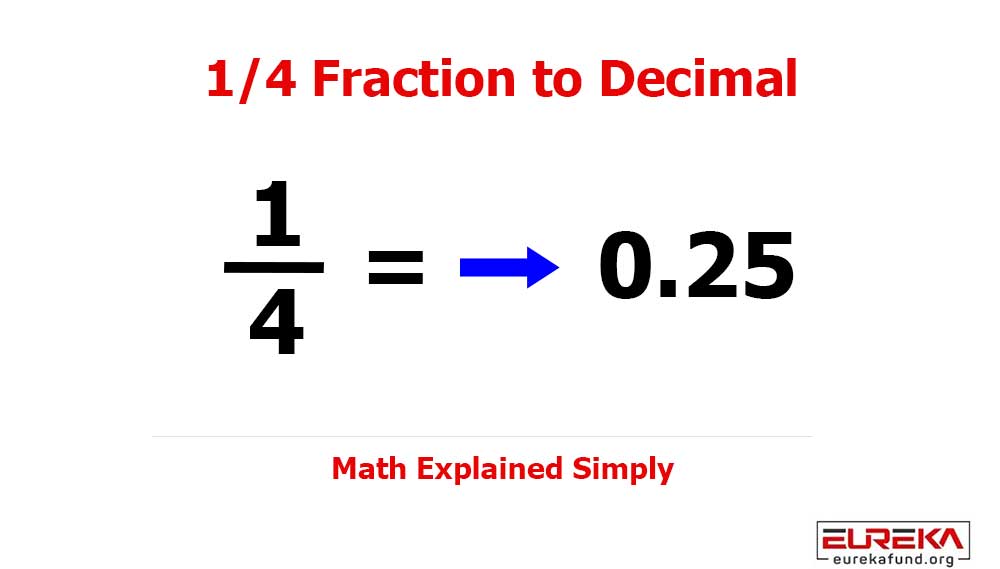
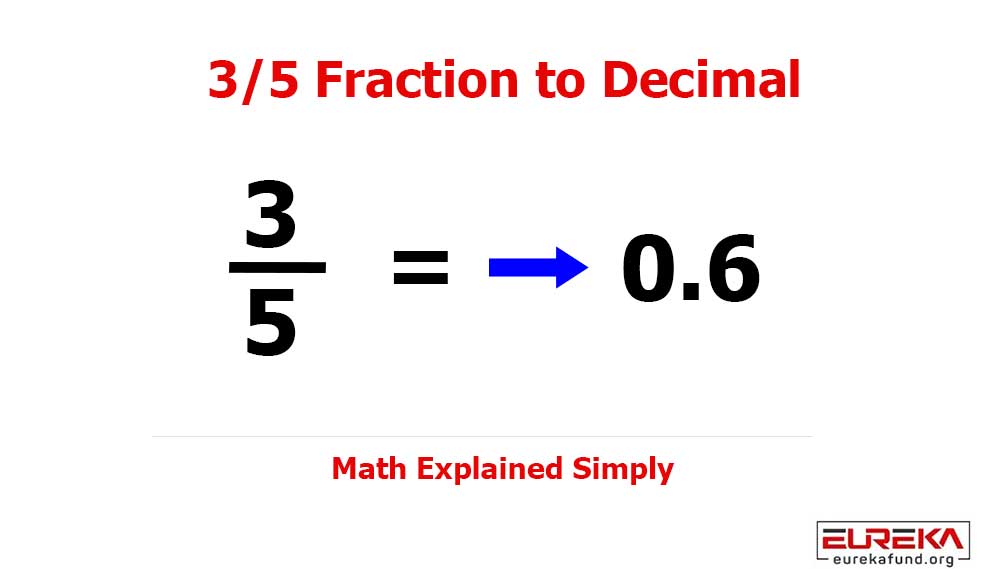
If you follow global innovation trends, you’ve likely heard the term Big Data everywhere — and for good reason.
In 2025, big data analytics has become a core driver for growth, innovation, automation, and digital transformation across industries.
But what exactly is big data?
How does it work?
And more importantly — how is it shaping the future of business, customer experience, and global technology?
Let’s break it down simply and powerfully.
Big data refers to the processing, management, and analysis of massive, diverse datasets using advanced tools such as AI, machine learning, predictive analytics, and cloud computing. The goal is to uncover hidden trends, solve complex problems, and anticipate future needs.
Data-driven companies are proven to be 23% more profitable and 19% more efficient than businesses that do not use analytics (Forbes Data & Analytics Report 2025).
Let’s explore how big data is shaping the future — and why every company must adopt it.
How Big Data Is Shaping the Future
1. Smarter & Stronger Risk Analysis
Risk analysis is essential for securing a company’s future — and big data makes it smarter, faster, and more accurate.
Using big data, organizations can:
- Track global market trends
- Analyze historical business patterns
- Segment data through clustering techniques
- Predict potential threats or downturns
- Identify vulnerabilities before they escalate

In 2025, companies using advanced analytics report a 40% improvement in risk mitigation and decision-making accuracy.
Big data transforms risk analysis from “guesswork” into data-backed strategy.
2. Improved Security & Fraud Protection
As digital transformation accelerates, cybersecurity risks have skyrocketed.
Big data analytics plays a major role in strengthening security.
Big Data Enables:
- Real-time threat detection
- Behavioral analysis of users
- Anomaly detection
- Machine-learning based fraud prevention
- Secure infrastructures for sensitive data
Security tools fueled by big data can analyze millions of records per second — identifying threats humans would never catch manually.
Many companies even outsource big data security to specialized firms who manage protection, analytics, and long-term data strategies to reduce risk and cost.
3. Better Customer Service & Experience
In today’s world, the fastest way to win customer trust is to make them feel understood and valued.
Big data helps companies deliver personalized, human-first experiences, such as:
- One-on-one real-time communication
- Personalized product recommendations
- Customer preference tracking
- Behavioral analysis for loyalty improvement
- Faster complaint resolution

Customer analytics software — often built by outsourced development teams — allows businesses to offer tailor-made services based on user history, behavior, and expectations.
Better insights = better experience and Better experience = stronger customer trust
4. Increased Revenue & Higher Business Value
Big data doesn’t just improve analytics — it directly increases revenue.
How big data boosts income:
- Predicts future customer needs
- Identifies profitable opportunities
- Improves product development
- Enhances marketing strategies
- Reduces operational waste
- Strengthens decision-making
Companies using big data grow faster, smarter, and more consistently, because they understand market changes long before competitors notice them.
Big data also reduces costs through:
- Early risk detection
- Fewer manual errors
- Faster operations
- One-time system automation
- Enhanced cybersecurity
In short, big data is not just a tech tool — it’s a profit engine.
Conclusion
Big data analytics is shaping the future by helping businesses think ahead, minimize risks, understand customers deeply, and operate with greater efficiency.
From risk analysis and security to customer service and revenue optimization, big data has become one of the most valuable assets for companies.
The biggest advantage of big data is its ability to predict future trends accurately — allowing businesses to prepare, adapt, and thrive in an increasingly competitive and technologically advanced world.
To stay relevant in the digital era, companies must integrate big data into their core strategies — or risk being left behind.