The decimal 0.6667 appears frequently in calculators, spreadsheets, statistics, and real-world calculations. At first glance, it may look like a simple terminating decimal — but in reality, 0.6667 is usually a rounded form of a repeating decimal.
This raises an important question:
What is 0.6667 as a fraction, and is it exact or approximate?
In this guide, we’ll convert 0.6667 into a fraction step by step, explain why it represents an approximation, verify the result, and show where this conversion is commonly used.
Why Convert 0.6667 into a Fraction?
Converting 0.6667 into a fraction helps when:
- Understanding rounded decimal values
- Working with ratios and proportions
- Interpreting calculator or spreadsheet results
- Comparing repeating decimals accurately
- Avoiding misunderstanding between exact and approximate values
Fractions clearly show whether a value is exact or estimated, which is crucial in math, finance, and data analysis.
Understanding the Decimal 0.6667
Before converting, it’s important to understand what 0.6667 represents.
- 0.6667 is a rounded decimal
- It approximates the repeating decimal 0.6666…
- The repeating decimal 0.6666… equals exactly 2/3
Because most calculators round to four decimal places, 0.6667 is commonly used as a rounded version of 2/3.
Method 1: Direct Decimal-to-Fraction Conversion
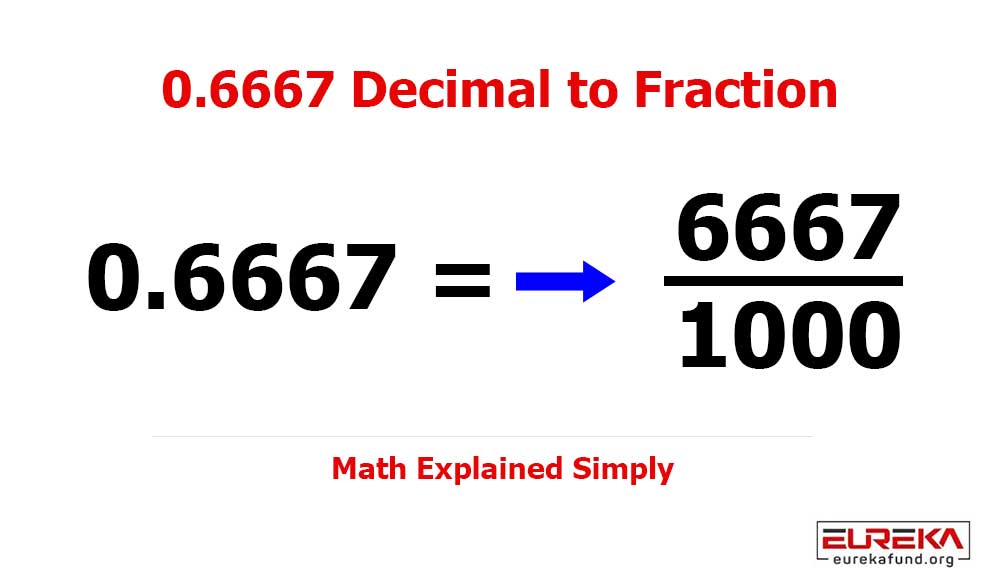
Step 1: Write 0.6667 as a Fraction
Since there are four digits after the decimal point, we place the number over 10,000:
0.6667 = 6667 / 10000
Step 2: Check for Simplification
To simplify, we check for common factors.
- 6667 is a prime number
- 10000 = 10 × 10 × 10 × 10
There are no common factors, so the fraction cannot be simplified.
✅ Result (Exact Fraction Form)
0.6667 = 6667 / 10000
This fraction is exact, but it represents an approximation, not a repeating value.
Method 2: Fraction Based on the Intended Value (Most Common Use)
In practical math, 0.6667 is almost always intended to represent 2/3.
Why?
- 2 ÷ 3 = 0.666666… (repeating)
- Rounded to four decimal places → 0.6667
So in most academic, financial, and statistical contexts:
0.6667 ≈ 2/3
✅ Most Commonly Accepted Fraction
0.6667 ≈ 2 / 3
✔ This is the fraction people usually mean when writing 0.6667.
Verification
Decimal Check
- 2 ÷ 3 = 0.666666…
- Rounded → 0.6667
✔ Matches the given decimal.
Exact vs Approximate — Important Distinction
| Decimal | Fraction | Type |
| 0.6667 | 6667/10000 | Exact (rounded value) |
| 0.6666… | 2/3 | Exact (repeating) |
👉 0.6667 is not exactly equal to 2/3, but it is an extremely close approximation.
Real-Life Uses of 0.6667 as a Fraction
📊 Data & Statistics
- Values rounded for reports or dashboards
- Displayed as 0.6667 instead of repeating decimals
💰 Finance
- Ratios approximated for pricing models
- Spreadsheet calculations rounded to four decimals
🎓 Education & Exams
- Often expected answer: 2/3
- Rounded decimals used in calculators
🧮 Probability
- A probability near two-thirds likelihood
- Easier to interpret as 2/3 than a long decimal
Common Mistakes to Avoid
- ❌ Assuming 0.6667 is exactly equal to 2/3
- ❌ Writing 0.6667 as 667/1000 (wrong precision)
- ❌ Ignoring rounding context
- ❌ Treating all decimals as terminating
Understanding rounding vs repeating is essential.
FAQs: 0.6667 as a Fraction
What is 0.6667 as a fraction?
Exact: 6667/10000
Common interpretation: 2/3
Is 0.6667 equal to 2/3?
Not exactly — it is a rounded approximation.
Why do calculators show 0.6667?
Because they round repeating decimals to a fixed number of digits.
Is 0.6667 a rational number?
Yes. All terminating decimals are rational numbers.
Which fraction should I use in exams?
Unless stated otherwise, 2/3 is the correct mathematical form.
✅ Final Answer Box
0.6667 as a Fraction
- Exact: 6667 / 10000
- Commonly Intended: 2 / 3
Key Takeaway
To convert 0.6667 into a fraction:
- Write it as 6667/10000 for exact precision
- Recognize it usually represents 2/3
- Understand the difference between rounded and repeating decimals
- Use 2/3 when an exact repeating value is expected
Knowing this distinction prevents mistakes in math, finance, exams, and data interpretation.
You may also find these related fraction examples helpful: